Income Gap Meaning In Economics

Income inequality is an economic concept that tends to hit some segments of populations harder than others with significant wage gaps often identified for women african americans and hispanics.
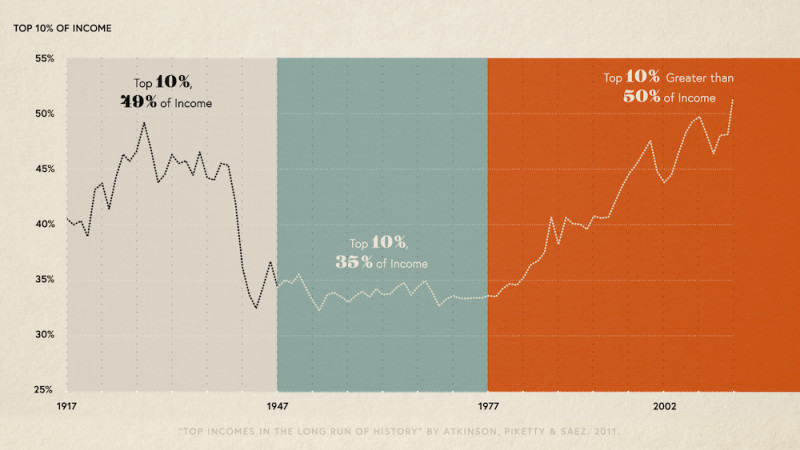
Income gap meaning in economics. A 2011 study titled divided we stand. 2016 mean income median income gap. Looked at in terms of the whole economy the commonest income gap is that between rich and poor with the rich usually being defined at the top 20 of income earners the top quintile and the poor the bottom 20 bottom quintile. Between the end of wwii and the 1970s the middle class grew and the income gap did not widen because americans in the working middle and upper classes were all reaping economic gains.
A gap analysis is the means by which a company can recognize its current state by measuring time money and labor and compare it to its target state. In broad strokes the income gap is the difference between the rich and the poor. To compare income inequality across countries the oecd uses the gini coefficient a commonly used measure ranging from 0 or perfect equality to 1 or complete inequality. Is the highest of all the g7 nations according to data from the organization for economic cooperation and development.
3 496 26 in montana the median household income only grew from 45 324 in 2011 to 48 380 in 2016. An income gap is a gap in income between one group and another. The poverty gap is a ratio showing the average shortfall of the total population from the poverty line the minimum level of income required to secure the basic necessities for survival. By 1991 it was eighty six to one.
In 1820 the ratio between the income of the top and bottom 20 percent of the world s population was three to one. Political discourse income inequality is often expressed as the gap between the 1 and the 99.