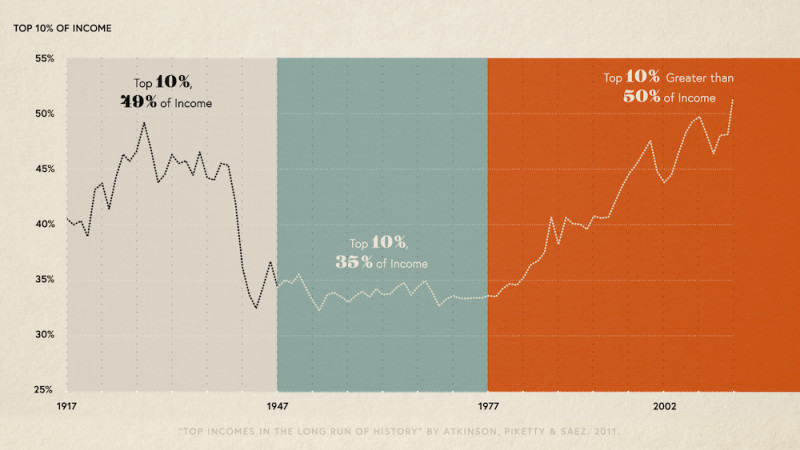
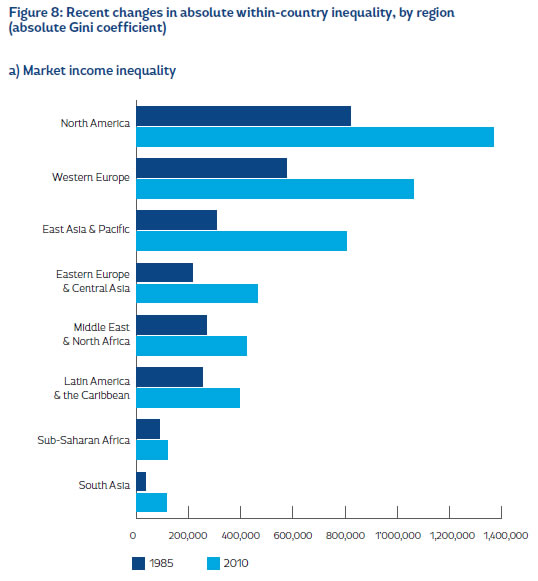
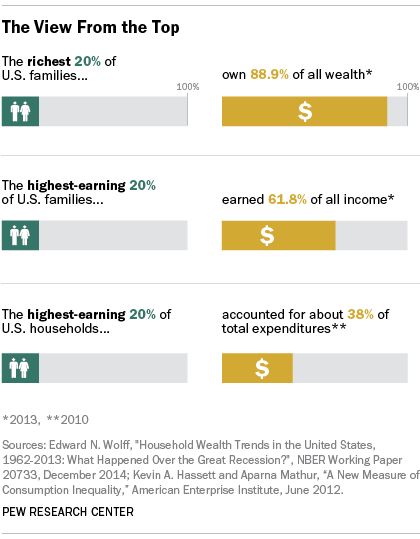
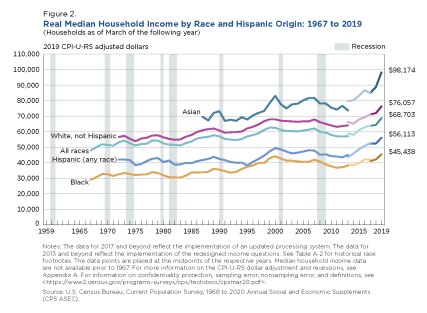
Income Inequality Definition Business

Income inequality refers to the varying incomes of different socioeconomic groups in an economy.
Income inequality definition business. Income inequality to the fore. Income is not the same as pay. Refers to how unevenly income is distributed in society. The issue of income inequality was in abeyance for the past decade as rising consumer debt concealed the true nature of income growth.
Second the cycles of gdp consumption and investment are. Income inequality is often accompanied by wealth. We sometimes refer to it as the income gap. Income inequality in economics significant disparity in the distribution of income between individuals groups populations social classes or countries.
Income includes all the money people receive from employment wages bonuses salaries etc. The analysis shows that income inequality is consistent with a smaller estimator of consumption and a greater estimator of investment. A survey of the evidence and some new results it is widely known that the business cycle has potentially important effects on the distribution of personal incomes. Income inequality is a major dimension of social stratification and social class.
Income inequality and the business cycle. In the coming decade the implications of rising income inequality will likely be far more apparent and are expected to have a significant impact on business strategy for companies. Economists and sociologists may measure income on a household or individual basis. For example work by mendershausen 1946 andkuznets 1953 foundthatthe income shares.
In many cases of economic inequality wealth flows disproportionately towards a small number of already financially well off individuals. Plus investments state benefits rent and pensions. The less equal the distribution the higher income inequality is. Income inequality the unequal distribution of income among the participants of an economy.
It highlights the gap between those with the highest and lowest incomes in a country region or the whole world.